If you are interested in the product and want more information, please leave your information .
Whatsapp : +86 15075770990
Wechat (China) : +86 15075770990
Email : sam@greatforming.com
Below is a brochure of our factory products, which can be viewed and downloaded.
Water-heated parking heater
I. Applications:
1. Starts various vehicle engines at low temperatures.
2. Provides heat for windshield defrosting and interior heating.
II. Function:
Heats the antifreeze fluid circulating in the vehicle engine, transferring heat directly to the radiator and defroster, providing a heat source for starting the engine at low temperatures and interior heating.
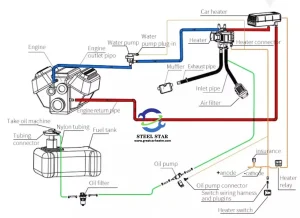
III. Installation: Connects in series with the engine’s circulation system.
The user sends a start signal via the remote control, an in-vehicle switch, or a timer. Upon receiving this signal, the device’s electronic control unit (ECU, whose core is a single-chip microcomputer) first checks basic conditions such as the vehicle’s battery voltage and coolant status. After confirming that there are no faults, it activates all components. Fuel Combustion: Independent Heat Generation
This is the source of heat, centered around “precise fuel injection + high-temperature ignition + complete combustion”:
The fuel pump draws fuel (diesel or gasoline, depending on the engine model) from the vehicle’s tank and pulses it, spraying fine droplets evenly onto the metal felt within the combustion chamber (avoiding direct fuel erosion and ensuring atomization).
Simultaneously, the glow plugs (or ignition pins) within the combustion chamber are rapidly heated to approximately 1000°C, vaporizing and igniting the atomized fuel, forming a stable flame.
The high-temperature exhaust gases generated by combustion are discharged outside the vehicle through a separate exhaust duct (completely isolated from the interior to prevent exhaust gas intrusion).
Heat Exchange: Coolant Heating
The combustion chamber is surrounded by a “coolant channel” (made of the same material as the engine cooling system pipes). The heat generated by the flame is rapidly transferred to the coolant within the channel, gradually raising the coolant temperature (typically a target temperature of 60-80°C, suitable for interior heating). Circulation Heat Transfer: Heat is transferred to the vehicle interior.
When the coolant temperature reaches a set value (generally 30-40°C), the electronic control unit activates the circulating water pump, pushing the heated coolant through a circuit consisting of the heater, engine radiator, and interior heater core.
When the hot coolant flows through the interior heater core, the heater (reusing the original vehicle’s air conditioner blower) starts, blowing the core’s heat into the vehicle interior, providing warmth.
At the same time, the circulating coolant preheats the engine, reducing wear during cold starts.

Small Water Heating Parking Heater Size
Technical Parameters
- Rated Voltage : 12V/24V (Can be customized according to your needs)
- Power : 5KW (Can be customized according to your needs)
- Fuel Consumption : About 0.38L/Hour
- Ambient Temperature : -40°~80°
- Product Weight : About 2.12KG
- Fuel Usage : Gasoline/Diesel/Methanol
Accessories List
Schematic

Brushless Motor
A brushless motor is a brushless DC motor. It’s actually a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) with an electronic commutator. It uses power electronics (inverter) to control the sequence of energizing the stator coils, generating torque to rotate the rotor. Compared to brushed motors, brushless motors offer advantages such as higher efficiency, longer life, lower noise, and reduced maintenance. However, they are more expensive and require a dedicated driver. They are widely used in automotive, home appliance, and aerospace applications.
Operating Principle
Electronic Commutation: Brushless motors eliminate mechanical brushes and commutators, instead using Hall sensors or other position detection methods to sense rotor position.
Drive Control: Based on the rotor position signal, the driver (or inverter) energizes the stator coils in a specific pattern, generating a rotating magnetic field.
Torque Generation: The permanent magnets on the rotor interact with the rotating magnetic field generated by the stator, generating torque to drive the rotor’s continuous rotation.
Advantages: High Efficiency and Low Power Consumption: Due to the lack of mechanical friction, brushless motors offer significantly higher efficiency and lower energy consumption than brushed motors.
Long Life: Without brush wear, the motor’s service life is significantly extended. Low Noise, Smooth Operation: The electronic commutation process is smoother, generating less noise and vibration.
High Reliability: The lack of brushes makes them less susceptible to environmental influences such as dust, resulting in more stable and reliable operation.
Low Maintenance Cost: No need to replace worn brushes, simplifying maintenance.
Disadvantages: High Cost: Due to the need for complex drivers and sensors, brushless motors are more expensive to manufacture than brushed motors.
Drive Required: Brushless motors must be used with a dedicated electronic controller to function properly; they are not a standalone power system.
Applications: Due to their superior performance, brushless motors are widely used in:
Home appliances: fans, air conditioners, washing machines
Automotive: electric vehicles, electronic power steering systems
Industrial equipment: robots, industrial automation equipment
Consumer products: model aircraft, drones, power tools, etc.
Remote Control For Remote Operation
1. Separate remote control.
2. Remote control within 50 meters.
3. Parameter settings and adjustments, multiple levels of adjustment, clear display brightness, and easy operation.



Website:
www.greatcarheater.com (English)
www.russianheater.com (Russian)
www.spanishheater.com (Spanish)



